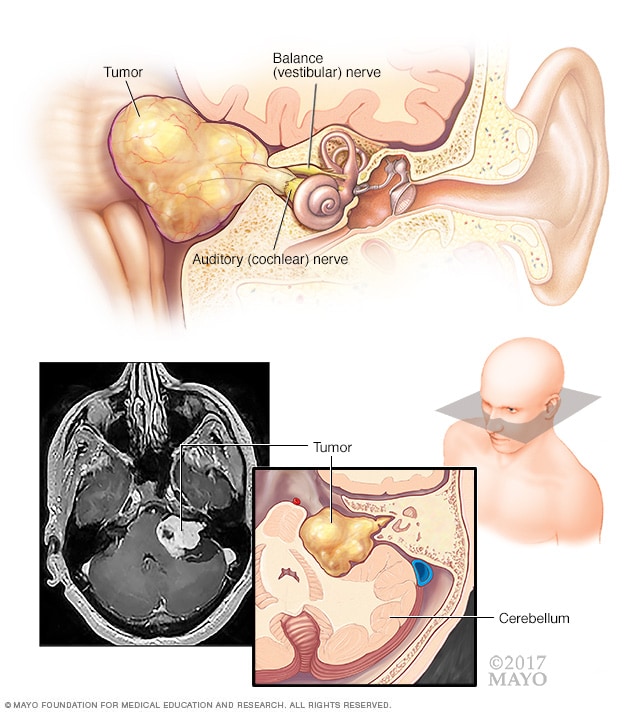
What is an acoustic neuroma?An acoustic neuroma (also known as vestibular schwannoma or acoustic neurinoma) is a benign (nonmalignant), usually slow-growing tumor that develops from the balance and hearing nerves supplying the inner ear.
Overview Vestibular schwannoma (VS)- incorrectly but more commonly known as acoustic neuroma or neurinoma- is a benign (non-cancerous) tissue growth resulting from an overproliferation of “schwann cells” constituting the eighth cranial nerve sheath.

Main Points: 1. Acoustic neuromas are a rare cause of unilateral hearing loss, dizziness, as well as other symptoms related to the brain.
General Discussion. An acoustic neuroma, also known as a vestibular schwannoma, is a rare benign (non-cancerous) growth that develops on the eighth cranial nerve.
Acoustic neuroma is a tumor that grows on the balance and hearing nerve in the head that may cause hearing loss.
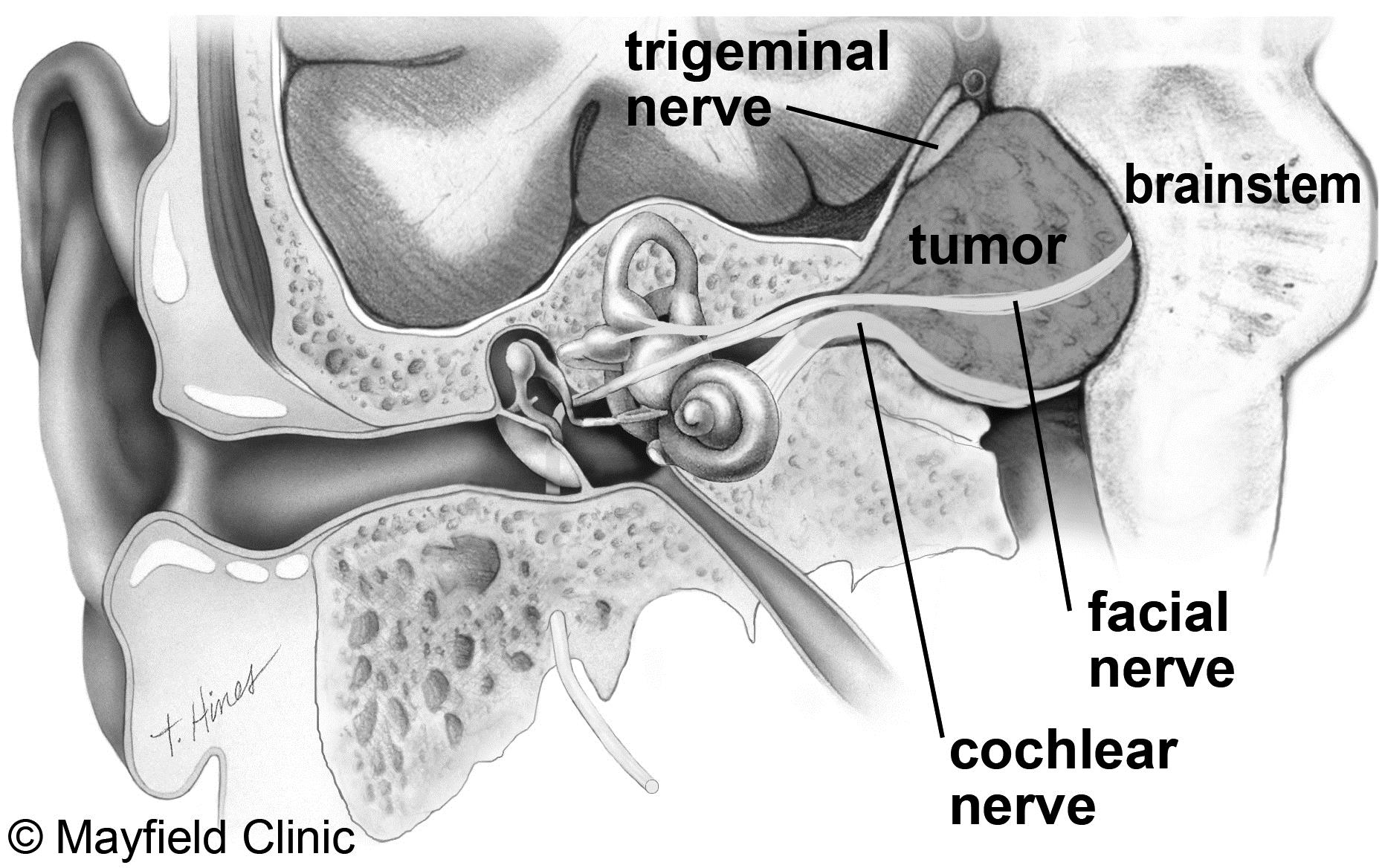

An acoustic neuroma is a skull based nerve sheath tumor that constitutes about 6% of all primary intracranial tumors. The are usually benign and slow growing tumor which arise primarily from the vestibular portion of the VIII cranial nerve and lie in the cerebellopontine angle – a wedge shaped area bounded by the petrous bone, the pons and the
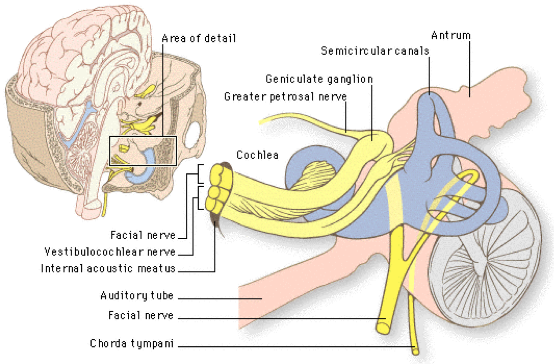

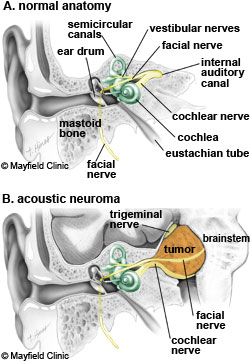
Anatomy of an Acoustic Neuroma. An acoustic neuroma, known as a vestibular schwannoma, is a benign (non-cancerous) growth that arises on the eighth cranial nerve leading from the brain to the inner ear.
Suboccipital surgery for acoustic neuroma Overview. A suboccipital craniotomy is a surgery performed to remove an acoustic neuroma growing from the nerve responsible for balance and hearing.
Acoustic neuroma: Introduction. Acoustic neuroma: A benign tumor of the 8th cranial nerve which lies in the tube connecting the inner ear to the brain. More detailed information about the symptoms, causes, and treatments of Acoustic neuroma is …